Running a local development server is an important feature of modern application development. For the purpose of building, testing, and debugging software before deployment, it helps developers start a production environment on their local computers.
We’ll walk you through the necessary steps and resources needed to set up and operate a local development server in this blog.
What is a Local Development Server?
You can run, test, and debug your applications on a local development server, which is an environment you set up on your own computer. It creates the actions of the real production server, helping you to:
- Identify and resolve issues early.
- Develop applications without internet connectivity.
- Test configurations safely before going live.
For instance, while developing a web application, using a local server enables you to render pages dynamically, process backend scripts, and test application logic in a controlled setup.
Why Setting Up a Local Dev Server is Essential
Developers use local servers for several practical reasons:
- Improved Workflow: Test code changes in real-time without delays.
- Consistency Across Environments: Ensure the app works the same way locally as it will in production.
- Faster Debugging: Quick identification and resolution of issues.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Share your development setup with team members for synchronized development.
How to Set Up a Local Development Server
Setting Up a Local Server with VS Code’s Live Server Extension
Steps:
- Install the “Live Server” extension from the Extensions Marketplace.
- Open your project folder in VS Code.
- Right-click on your HTML file and select “Open with Live Server.”
- The application will open in your browser at http://127.0.0.1:5500/.
This tool automatically reloads your browser whenever you save your files, speeding up development.
Using Node.js for a Lightweight Server
Node.js is a JavaScript runtime used for server-side development.
- Installation: Download and install Node.js.
- Initialize a Node.js Project:
Installation: Download and install Node.js.

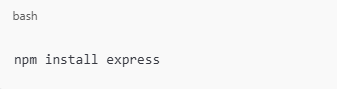
Install Express:
Create a server:
Create a file server.js and add:
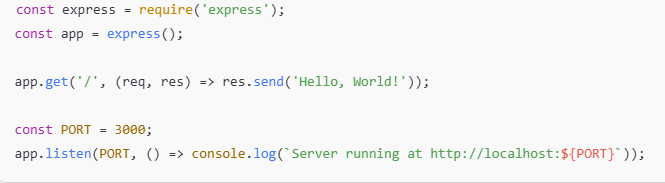
Run the server:

Node.js in Frontend Development
Node.js is integral to front-end frameworks like React and Vue. You can set up a local development environment with a single command:
React:

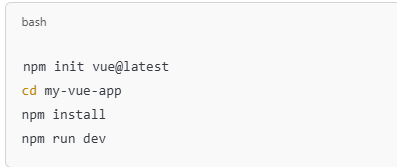
Vue:
Node.js is an excellent choice for developers looking for a quick and efficient solution to test JavaScript-heavy applications.
Running a Server with Python’s HTTP Module
Python makes it easy to set up a basic HTTP server for testing or development purposes. Below is a guide to running a server with the built-in http.server module.
Steps:
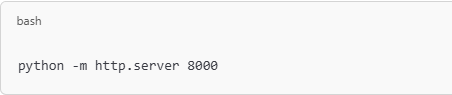
Start the ServerRun the following command in your terminal to start a simple HTTP server:
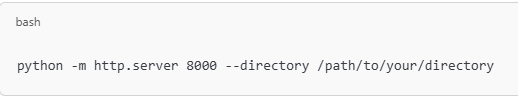
Serve a Specific Directory To serve files from a specific directory, use this command:
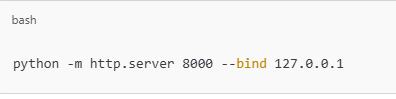
Restrict Access to Localhost
Bind the server to localhost for restricted access:
Create a Custom HTTP Server Script
Use the following Python script for a custom HTTP server:

Save it as server.py and run:

Stop the Server
Press Ctrl + C in the terminal to stop the server.
. Visit http://localhost:8000 in your browser.
This method is ideal for projects that don’t require advanced backend capabilities.
Setting Up a Server Using PHP
Setting up a local server on Ubuntu for Laravel involves installing and configuring the necessary tools like PHP, Composer, and a web server (Apache or Nginx). Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Steps:
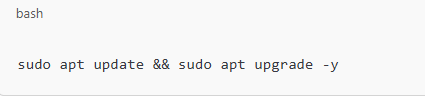
Update System Packages
Install Required Software
Laravel requires PHP, composer, and a database server like MySQL. We’ll also install Apache.
Install Apache

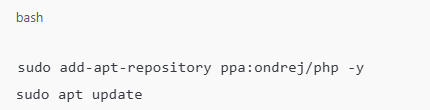
Install PHP
Laravel requires PHP 8.1 or later (check Laravel’s documentation for the exact version).
sudo apt install php8.1 php8.1-cli php8.1-mbstring php8.1-xml php8.1-bcmath php8.1-curl php8.1-zip php8.1-intl php8.1-mysql -y
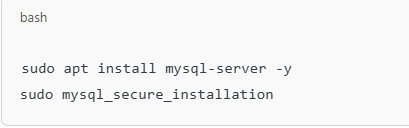
Install MySQL
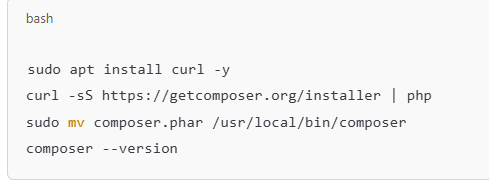
Install Composer
Composer is a dependency manager for PHP.
Set Up Laravel
Download Laravel Project
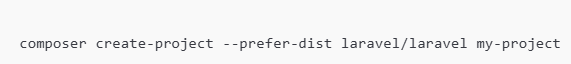
If you’re creating a new Laravel project:
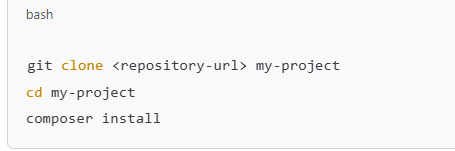
If you’re cloning an existing Laravel project:
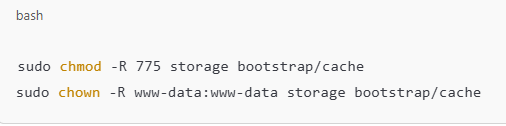
Set Permissions
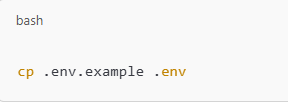
Create .env File
Copy the example .env file:
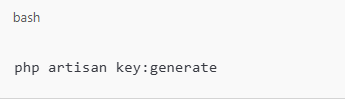
Generate the application key:
Set the correct database credentials in the .env file
Purpose: Test server-side functionality without deploying to a live server.
PHP servers are popular for WordPress developers and other PHP-based applications.
. Testing Across Devices
To test your local server on multiple devices:
- Ensure all devices are connected to the same Wi-Fi network.
- Find your machine’s IP address.
- Replace localhost with your IP address in the URL, e.g., http://192.168.1.5:8000.
This setup is particularly useful for testing responsiveness and compatibility on mobile devices.
. Advanced Tools for Robust Local Server Management
For larger or more complex projects, consider these advanced tools:
- Docker: Containerizes your application for consistent performance across environments.
- Vite: A modern development server tailored for frameworks like React, Vue, and Svelte.
- Google Cloud SDK: Ideal for developers using Google App Engine.
. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Encountering problems with your local server? Here are some quick fixes:
- Port Already in Use: Change the port in your command (e.g., -p 8001).
- Firewall Restrictions: Temporarily disable your firewall or create an exception for the server’s port.
- Outdated Tools: Make sure Node.js, Python, or PHP is updated to the latest version.
Local Servers and Continuous Development
Local development servers also play a vital role in:
- Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): Automate your pipeline with tools like Docker Compose.
- Automated Testing: Simulate production environments for end-to-end testing.
- Scaling with Docker: Use Docker containers to scale services efficiently.
Conclusion:
To sum up, a local development server is a necessary tool for modern application development. Before deploying, it gives developers the freedom to test, debug, and improve their apps in a regulated production-like setting. Developers can optimize their workflow, detect and address problems early, and ensure consistency across several settings by utilizing either advanced tools like Docker and Vite or more lightweight servers like Node.js, Python, or PHP.
Local development servers are necessary for effectively creating strong, dependable applications because they can also integrate into continuous development pipelines and test across various devices.
FAQs
Q1. What is a local development server?
Before moving apps to a production server, they are tested and debugged on your computer using a local development server.
Q2. Can I use a local server without an internet connection?
Yes, local servers run entirely on your machine and don’t require internet access.
Q3. How do I know that my server is working?
Visit the local server URL (e.g., http://localhost:8000) in your browser. If it loads your app or a test page, it’s working.
Q4. Can I run multiple servers at once?
Yes, you can run multiple local servers on different ports (i.e.,http://localhost:8000 and http://localhost:8001).
Q5. If my server isn’t loading, what should I do?
Make sure your firewall isn’t preventing the connection, confirm the port number, and see if the server is operational.












